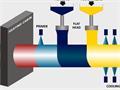
Notes of galvanized steel pipe when welding
تاريخ:2018-03-29
رأي:2907
First, the prerequisite must be polished
However, the galvanized layer at the weld must be polished away, otherwise bubbles, trachoma, false welds, etc. will be generated. It also makes the welds brittle and their rigidity decreases.
Second, the galvanized steel welding characteristics
Galvanized steel is generally coated with a layer of zinc outside the low carbon steel. The galvanized layer is generally 20 um thick. Zinc has a melting point of 419°C and a boiling point of about 908°C. In welding, zinc melts into a liquid that floats on the surface of the bath or at the root of the weld. Zinc has a greater solid solubility in iron, zinc liquids will penetrate the weld metal deeper along the grain boundaries, and low-melting-point zinc will form "liquid metal embrittlement."
At the same time, zinc and iron can form intermetallic brittle compounds. These fragile phases reduce the plasticity of the weld metal and cause cracks under tensile stress.
If the welding fillet weld, especially the T-joint fillet weld, is most likely to produce penetration cracks. When the galvanized steel is welded, the zinc layer on the surface and edge of the groove will be oxidized, melted, evaporated, and even emit white fumes and steam under the action of the arc heat, and the pores of the weld can easily be caused.
ZnO formed due to oxidation, its melting point is higher, about 1800 °C above, if the parameters in the welding process is too small, will cause ZnO slag, at the same time. As Zn becomes a deoxidizer. FeO-MnO or FeO-MnO-SiO2 low-melting oxide slags are generated. Secondly, due to the evaporation of zinc, a large amount of white fumes are volatilized, which has a stimulatory and harmful effect on the human body. Therefore, the galvanized layer at the welding place must be ground off.
Third, the welding process control
The pre-welding preparation of galvanized steel is the same as that of ordinary low-carbon steels. It should be noted that the size of the groove and the nearby galvanized layer must be carefully handled. For penetration, the groove size should be appropriate, generally 60 ~ 65 °, to leave a certain gap, usually 1.5 ~ 2.5mm; In order to reduce the penetration of zinc on the weld, before welding, the galvanized within the groove The layer is removed and then soldered.
In the actual supervision work, the use of a concentrated beating, no blunt edge process for centralized control, two welding processes, reducing the possibility of incomplete penetration.
The electrode should be selected according to the material of the base material of the galvanized pipe. Generally, low-carbon steel is widely used due to the ease of operation.
Welding methods: When welding the first layer of multilayer welding, as much as possible to make the zinc layer to melt and vaporize, evaporation and escape the weld, can greatly reduce the liquid zinc left in the weld.
However, the galvanized layer at the weld must be polished away, otherwise bubbles, trachoma, false welds, etc. will be generated. It also makes the welds brittle and their rigidity decreases.
Second, the galvanized steel welding characteristics
Galvanized steel is generally coated with a layer of zinc outside the low carbon steel. The galvanized layer is generally 20 um thick. Zinc has a melting point of 419°C and a boiling point of about 908°C. In welding, zinc melts into a liquid that floats on the surface of the bath or at the root of the weld. Zinc has a greater solid solubility in iron, zinc liquids will penetrate the weld metal deeper along the grain boundaries, and low-melting-point zinc will form "liquid metal embrittlement."
At the same time, zinc and iron can form intermetallic brittle compounds. These fragile phases reduce the plasticity of the weld metal and cause cracks under tensile stress.
If the welding fillet weld, especially the T-joint fillet weld, is most likely to produce penetration cracks. When the galvanized steel is welded, the zinc layer on the surface and edge of the groove will be oxidized, melted, evaporated, and even emit white fumes and steam under the action of the arc heat, and the pores of the weld can easily be caused.
ZnO formed due to oxidation, its melting point is higher, about 1800 °C above, if the parameters in the welding process is too small, will cause ZnO slag, at the same time. As Zn becomes a deoxidizer. FeO-MnO or FeO-MnO-SiO2 low-melting oxide slags are generated. Secondly, due to the evaporation of zinc, a large amount of white fumes are volatilized, which has a stimulatory and harmful effect on the human body. Therefore, the galvanized layer at the welding place must be ground off.
Third, the welding process control
The pre-welding preparation of galvanized steel is the same as that of ordinary low-carbon steels. It should be noted that the size of the groove and the nearby galvanized layer must be carefully handled. For penetration, the groove size should be appropriate, generally 60 ~ 65 °, to leave a certain gap, usually 1.5 ~ 2.5mm; In order to reduce the penetration of zinc on the weld, before welding, the galvanized within the groove The layer is removed and then soldered.
In the actual supervision work, the use of a concentrated beating, no blunt edge process for centralized control, two welding processes, reducing the possibility of incomplete penetration.
The electrode should be selected according to the material of the base material of the galvanized pipe. Generally, low-carbon steel is widely used due to the ease of operation.
Welding methods: When welding the first layer of multilayer welding, as much as possible to make the zinc layer to melt and vaporize, evaporation and escape the weld, can greatly reduce the liquid zinc left in the weld.