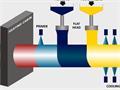
Factors on Affecting the Compressive Strength of Steel
تاريخ:2017-01-05
رأي:2721
In the long-distance transmission of natural gas, the pipeline in the deep sea under the pressure of resistance to external water pressure, so the general use of UOE pipe. UOE steel pipe manufacturing methods for the cold stamping method, the strength of steel anisotropy. In order to predict the compressive strength of UOE steel pipe and to find out the crushing mechanism of the steel pipe, Nippon Steel has carried on the numerical simulation analysis of steel pipe forming-performance evaluation. The numerical simulation is composed of two-dimensional forming model of steel pipe and three-dimensional crushing model of steel pipe which reflects the shape and residual stress.
1. Strength anisotropy and residual atress of UOE steel
As we all know, the factors that affect the compressive strength of steel pipe shape (pipe roundness and uneven wall thickness), yield strength (YS) and residual stress. The compressive yield strength in the circumferential direction and the residual stress have a great relationship with each other. The yield strength distributions of the wall sections measured for round bars and cylindrical specimens (both 6 mm in diameter) show that the decrease in the compressive yield strength in the circumferential direction of the steel pipe is particularly pronounced. The comparison of the S-S curves in the wall thickness position shows that a circular S-S curve originates from the wall thickness center and externally due to the Bauschinger effect of elastic deformation. According to the comparison of UOE steel pipe and seamless steel pipe for oil well, the residual stress of the two kinds of steel pipe tends to be compressed inside, but the residual stress of UOE steel pipe is small.
2. Numerical simulation
In the process of numerical analysis, an integrated model was used to evaluate the forming-compressive strength of UOE steel tubes. In the forming model of the UOE steel pipe (two-dimensional plane deformation element), the S-S curve of the plate is used and the residual stress is applied to the crush model (three-dimensional solid element). The semi-experimental method (simulated deformation test) is used to predict the S-S curve because it is difficult to precisely predict the S-S curve change from plate to steel pipe only by numerical analysis and simulation. That is, the calculated equivalent plastic strain hysteresis is applied to the rod sample sampled from the plate, and then the compressed S-S curve obtained for each wall thickness position is defined.
1. Strength anisotropy and residual atress of UOE steel
As we all know, the factors that affect the compressive strength of steel pipe shape (pipe roundness and uneven wall thickness), yield strength (YS) and residual stress. The compressive yield strength in the circumferential direction and the residual stress have a great relationship with each other. The yield strength distributions of the wall sections measured for round bars and cylindrical specimens (both 6 mm in diameter) show that the decrease in the compressive yield strength in the circumferential direction of the steel pipe is particularly pronounced. The comparison of the S-S curves in the wall thickness position shows that a circular S-S curve originates from the wall thickness center and externally due to the Bauschinger effect of elastic deformation. According to the comparison of UOE steel pipe and seamless steel pipe for oil well, the residual stress of the two kinds of steel pipe tends to be compressed inside, but the residual stress of UOE steel pipe is small.
2. Numerical simulation
In the process of numerical analysis, an integrated model was used to evaluate the forming-compressive strength of UOE steel tubes. In the forming model of the UOE steel pipe (two-dimensional plane deformation element), the S-S curve of the plate is used and the residual stress is applied to the crush model (three-dimensional solid element). The semi-experimental method (simulated deformation test) is used to predict the S-S curve because it is difficult to precisely predict the S-S curve change from plate to steel pipe only by numerical analysis and simulation. That is, the calculated equivalent plastic strain hysteresis is applied to the rod sample sampled from the plate, and then the compressed S-S curve obtained for each wall thickness position is defined.